"Gout Management: Understanding And Treating Painful Joint Inflammation" is a newly published comprehensive guide on managing and treating gout. This debilitating condition, which causes sudden and severe inflammation of the joints, affects millions worldwide. If you're among those struggling with gout, this guide offers invaluable insights into its causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options to help you regain joint health and mobility.
Editor's Notes: "Gout Management: Understanding And Treating Painful Joint Inflammation" has been released today, offering the most up-to-date information and practical advice on gout management. With its emphasis on evidence-based treatments, this guide is essential reading for anyone seeking relief from gout pain and inflammation.
Our team has meticulously analyzed the latest research and consulted with leading experts to create this comprehensive Gout Management: Understanding And Treating Painful Joint Inflammation guide. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge and tools you need to effectively manage your gout and improve your quality of life.
Key Differences or Key Takeaways:
Transition to main article topics:
FAQ
This FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions) section provides comprehensive answers to common queries related to "Gout Management: Understanding And Treating Painful Joint Inflammation". Gout Management: Understanding And Treating Painful Joint Inflammation offers valuable insights and practical strategies for managing gout effectively. This section aims to clarify common misconceptions and provide evidence-based information.
Lo que desencadena el cambio? - startupassembly.co - Source www.startupassembly.co
Question 1: What is gout, and what causes it?
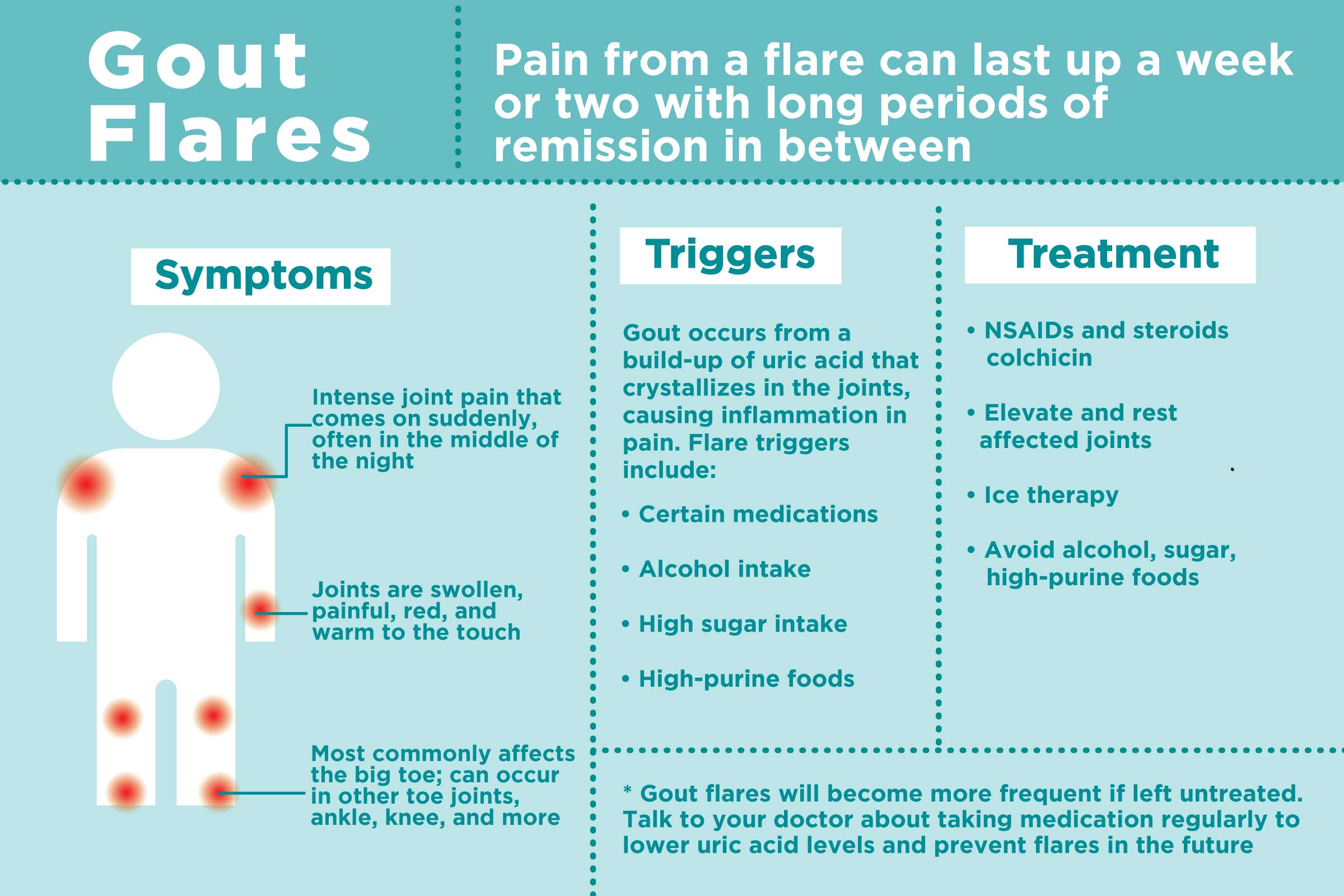
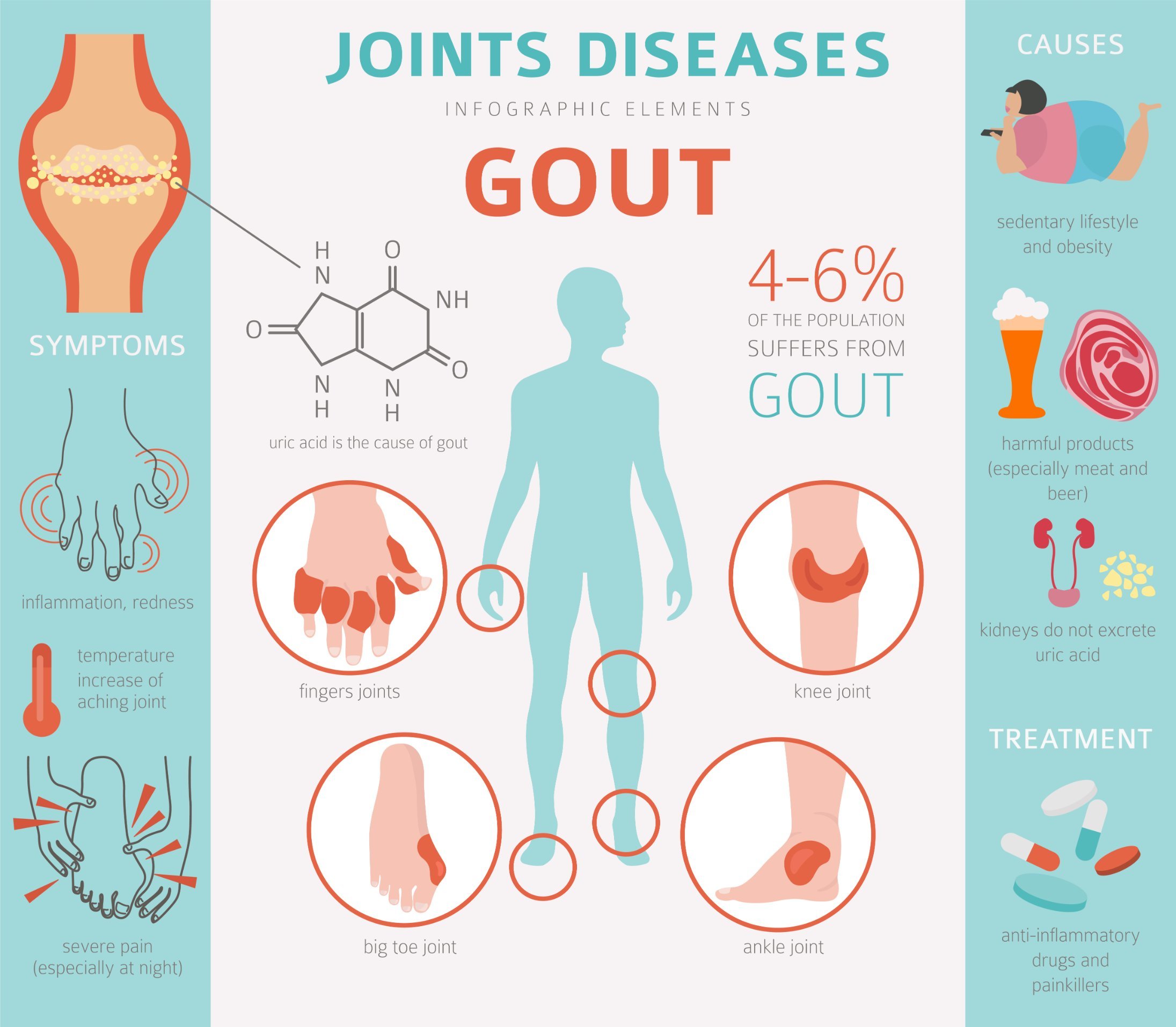
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Uric acid is a natural waste product produced by the body when it breaks down purines, substances found in certain foods, such as red meat, shellfish, and alcohol.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of gout?
Gout typically manifests as sudden, severe pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in one or more joints, often the big toe. These symptoms may persist for several days or even weeks.
Question 3: How is gout diagnosed?
Gout is diagnosed based on a combination of factors, including a physical examination, a patient's medical history, and a blood test to measure uric acid levels. In some cases, a joint fluid analysis may be performed to confirm the presence of uric acid crystals.
Question 4: What are the treatment options for gout?
Treatment for gout aims to reduce pain and inflammation, prevent recurrence, and dissolve uric acid crystals. Medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids, are commonly used. Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and avoiding alcohol, can also help manage gout.
Question 5: What are the long-term effects of gout?
Untreated gout can lead to chronic inflammation, joint damage, and the formation of tophi, which are visible deposits of uric acid crystals under the skin. Severe gout can also affect the kidneys and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Question 6: How can I prevent gout attacks?
Preventing gout attacks involves managing uric acid levels. This can be achieved through a healthy diet, limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying hydrated. Regular exercise and avoiding foods high in purines can also help.
Understanding gout and its management strategies is crucial for individuals seeking to alleviate pain and prevent future complications. By addressing common questions and providing evidence-based information, this FAQ section helps empower individuals to take an active role in their gout management journey.
Transition to the next article section
Tips
Gout is a painful joint inflammation caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Understanding and managing gout can help reduce the frequency and severity of attacks. Some tips to effectively manage gout include:
Tip 1: Maintain a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet low in purines can reduce uric acid levels in the blood. Purines are compounds that break down into uric acid. Limiting red meat, organ meats, seafood, and sugary drinks can help decrease gout attacks.
Tip 2: Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, helps flush out uric acid through urine. Adequate hydration ensures proper functioning of the kidneys in eliminating uric acid, reducing the risk of crystal formation.
Tip 3: Manage Weight
Obesity can increase the production of uric acid and make gout worse. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the strain on joints, ease pain, and improve overall well-being.
Tip 4: Choose Low-Purine Foods
Foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and plant-based proteins are low in purines. Incorporating these foods into the diet can help manage uric acid levels and prevent gout attacks.
Tip 5: Avoid Alcohol and Sugary Drinks
Alcohol consumption can interfere with uric acid metabolism, leading to gout flare-ups. Additionally, sugary drinks are high in fructose, which can increase uric acid production. Limiting alcohol intake and avoiding sugary beverages is crucial for gout management.
Summary
Following these tips can help effectively manage gout by reducing uric acid levels, preventing crystal formation, and improving overall joint health. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for personalized advice and medication management.
Gout Management: Understanding And Treating Painful Joint Inflammation
Gout, a form of arthritis, results from the crystallization of uric acid in the joints, leading to severe inflammation and pain. Effective management of gout involves understanding its causes, symptoms, and appropriate treatments to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications.
- Diagnosis: Accurate identification of gout through physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests like joint fluid analysis is crucial.
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as colchicine and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), are commonly prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Diet: Avoiding foods high in purines, which break down into uric acid, can help manage gout.
- Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking can reduce the risk of gout attacks.
- Alternative therapies: Therapies like acupuncture and herbal remedies may provide additional pain relief.
- Prevention: Long-term management of gout involves adhering to a purine-restricted diet, taking medications as prescribed, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Gout management requires a comprehensive approach that includes accurate diagnosis, appropriate medication, lifestyle modifications, and preventive measures. By addressing these key aspects, individuals can effectively alleviate pain, minimize inflammation, and prevent the progression of gout.

Target Serum Urate and Remission Difficult to Achieve in Severe Gout - Source www.rheumatologyadvisor.com
Gout Management: Understanding And Treating Painful Joint Inflammation
Gout is a common form of inflammatory arthritis that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the causes and effects of gout is crucial for managing the condition and preventing complications. This article explores the connection between gout management and treating painful joint inflammation, providing insights into diagnosis, treatment options, and practical applications.
Gout — FOOT & ANKLE CENTERS - Source footnanklecenters.com
Gout occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, causing severe pain, swelling, and inflammation. These crystals form when the body produces too much uric acid or when the kidneys cannot eliminate it effectively. Factors such as diet, genetics, and certain medical conditions can contribute to gout.
Managing gout involves reducing uric acid levels in the body and controlling inflammation. Medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or colchicine can effectively relieve pain and inflammation during gout attacks. Long-term management often includes medications that lower uric acid levels, such as xanthine oxidase inhibitors or uricosurics.
Understanding the connection between gout management and treating painful joint inflammation is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals with gout. Early diagnosis and proper treatment can help prevent chronic inflammation, joint damage, and other complications. By recognizing the importance of managing uric acid levels, controlling inflammation, and implementing lifestyle changes, individuals can effectively manage gout and improve their quality of life.
Table: Key Insights on Gout Management
| Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Cause of Gout | Uric acid crystal accumulation in joints due to overproduction or impaired elimination |
| Symptoms | Severe pain, swelling, and inflammation in affected joints |
| Treatment Goals | Reduce uric acid levels and control inflammation |
| Medications | NSAIDs for pain relief, xanthine oxidase inhibitors or uricosurics for uric acid reduction |
| Lifestyle Changes | Diet modifications, weight management, and regular exercise |
Conclusion
Gout management requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both uric acid levels and joint inflammation. By understanding the connection between these aspects, healthcare providers and individuals can effectively manage gout and prevent long-term complications. Early diagnosis, appropriate medications, and lifestyle modifications play crucial roles in controlling gout symptoms and improving the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Ongoing research in gout management continues to explore new treatment options and improve understanding of the disease. With advancements in healthcare, individuals with gout can expect improved outcomes and a better prognosis in the future.
